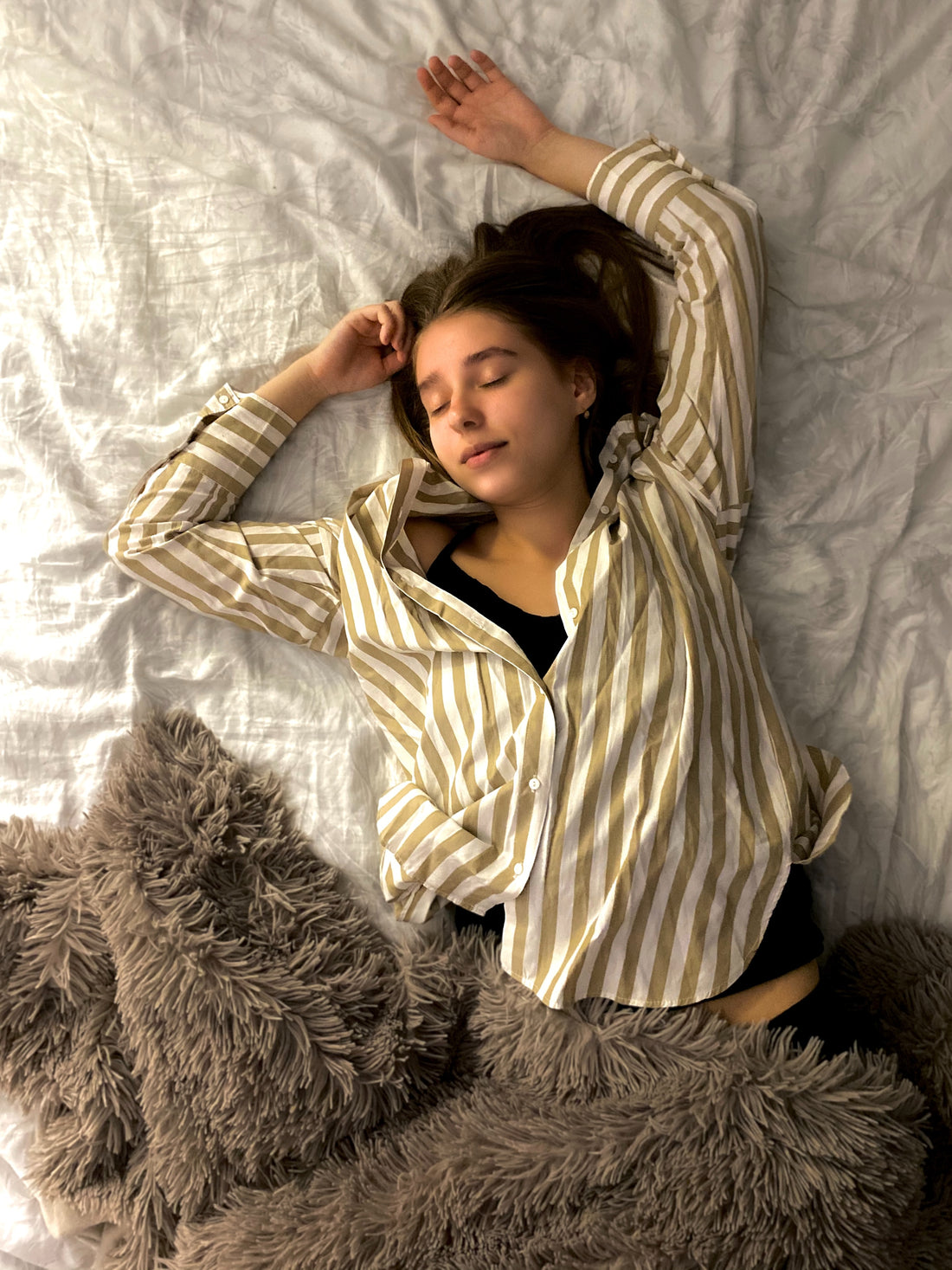
We all tend to take a good night's sleep for granted. But when we don’t get those 8 hours, all hell breaks loose. This holds true, especially if you have chronic insomnia.
However, good sleep hygiene practices and behavioral changes are known to target underlying symptoms of insomnia and improve your sleep quality. Some people also swear by prescription drugs that provide relief.
This article explores how sleep hygiene practices and prescribed allopathic medications help cure insomnia.
But what out of the two ways is better? What will permanently keep those symptoms at bay instead of simply providing a quick fix? Let’s find out.
What Is Insomnia?
Insomnia is a sleep-related disorder that causes a person to experience difficulty going to bed or staying asleep. People may suffer from acute or short-term insomnia and chronic insomnia.
Insomnia results in fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and an overall sense of confusion and brain fog. Over the years, it can also significantly reduce the quality of your life as it slowly chips away at the immune system’s ability to fight.
More serious ramifications of insomnia include increased susceptibility to heart disease, obesity, and high blood pressure.
Many factors, including anxiety, depression, trauma, grief, chronic stress, and major lifestyle changes, can cause insomnia. Mental health disorders are the most common cause of insomnia.
Let’s take a look at two main ways we can combat insomnia symptoms and improve the quality of our sleep.
Benefits Of Medication
Allopathic medications work wonders for treating sleep-related disorders. While there’s no doubt that they promote relief, they come with many disclaimers and side effects.
The FDA has approved a class of medications known as sedative-hypnotic drugs for insomnia treatment. Zolpidem, triazolam, trazodone, and quazepam are a few common ones. Benzodiazepines are a class of sleeping pills prescribed for short-term relief from sleep deprivation.
How Do These Drugs Work?
Benzodiazepines and zolpidem have a sedative effect on us. They work by increasing the effects of GABA in our bodies, causing our muscles to relax by reducing anxiety and adrenaline. GABA, or gamma-aminobutyric acid, helps regulate emotions, memory, and breathing.
In short, most medications used to treat insomnia work by targeting and slowing down receptors in the nervous system.
While these solutions are very effective, they also cause serious side effects and interact negatively with other drugs or substances. Some of these drugs are chemically habit-forming, which means you can develop addictions to them.
Overdosing and taking sleeping pills longer than prescribed can result in dizziness, dry mouth, brain fog, increased tolerance to the drug, difficulty with motor coordination, and an unsteady gait.
It can lead to addiction and cause mental health disorders. In severe cases, abuse of these drugs can be life-threatening.
When Is It Okay To Take Medication?
This is not to say that medication is not important. When insomnia takes over your life and turns into a vicious cycle, sometimes, the only way to break it is by visiting a sleep clinic and getting a prescription from a medical professional.
Medications provide relief, giving us the tools to work holistically to cure insomnia. Regular counseling and psychiatric medication work well together if you have mental health disorders that can cause insomnia.
It’s always important to supplement medication with lifestyle changes. Drugs only go as far as treating the symptoms, but behavioral changes and good sleep hygiene can address the root cause of your insomnia.
Benefits Of Sleep Hygiene
Sleep hygiene is the practice of implementing behaviors that promote a good night’s sleep. It entails altering environmental conditions, incorporating alternative therapies, and changing habits to manage insomnia.
Here are some ways to ensure good sleep hygiene.
Guided Meditation
Guided meditations and mindfulness help us focus on breathing to alleviate stress and tense muscles. Incorporating a five-minute guided meditation into your daily bedtime routine can lower your heart rate and reduce shallow breathing.
Quitting Unhealthy Habits
Before you protest, hear us out. If you’re a regular smoker and consume alcohol frequently, you might want to start thinking about reducing these habits to maybe once a week.
While alcohol is a sedative, prolonged use can cause disruptions in your sleep cycle. It can suppress your REM sleep, the deep sleep most important for our bodies. Alcohol consumption can set you up to develop insomnia, even if you don’t have it already!
If you drink coffee, finish your last cup of the day before 5 pm. The stimulant effects of caffeine can last for hours after consumption.
Avoid eating a large meal right before bedtime; it can interfere with a full sleep cycle. Give your body two or three hours to digest your dinner before hitting the hay.
Environmental Changes
Lower your lights at least an hour before bed. Watching TV, working on your laptop, or scrolling on your phone is not a good idea if you’re winding down. The screen brightness tricks your brain into thinking it’s still daytime, so you don’t feel sleepy.
Keeping your room cool, quiet, and dark will communicate to your body to kick-start drowsiness.
Sometimes, respiratory disorders can interfere with deep sleep. Intuitive products are available for sleep and respiration therapy to help with ventilation and promote deep sleep.
Relaxing Music
Believe it or not, research states that music therapy is very effective in treating insomnia. The repetitive notes, slow rhythms, and soft beats can induce a sedative effect. It’s like someone singing a lullaby to get a child to sleep—adults can benefit from it too!
Several people also use white noise to help them calm down. Sometimes, a stark quietness can be disturbing. Hearing a fan rotate or the gentle pitter-patter of rain can help you relax.
Using Youtube to find white noise sounds is a cost-effective way to manage insomnia.
Aromatherapy
Anxiety, fatigue, and heavy stressors worsen our sleep quality. Aromatherapy is a great alternative way to help reduce these negative feelings. Essential oils like lavender, chamomile, jasmine, and peppermint are inexpensive ways to promote sleep.
The active ingredients in lavender, like linalyl acetate, are known to reduce nervous system activity, lower heart rate, and trigger emotional responses to aid better sleep!
Conclusion
To sum up, there are significant benefits to using medication and sleep hygiene practices to cure insomnia. Medication should be used to treat serious, chronic conditions and only to supplement good sleep hygiene practices.
Implementing lifestyle and behavioral changes is ultimately the most effective way to successfully manage and prevent insomnia.